Radon, a colorless, odorless, and tasteless radioactive gas, poses a significant health risk to individuals exposed to elevated levels. Understanding how radon affects health is crucial for mitigating its harmful effects and safeguarding well-being.
This article delves into the intricate relationship between radon exposure and health, exploring the risks, implications, and mitigation strategies associated with this silent threat.
Table of Contents
Understanding Radon Exposure
Radon is a naturally occurring gas that results from the decay of uranium in soil, rock, and water.
When radon is released from the ground, it can seep into buildings through cracks in the foundation, gaps in floors, walls, and other openings, accumulating to potentially dangerous levels.
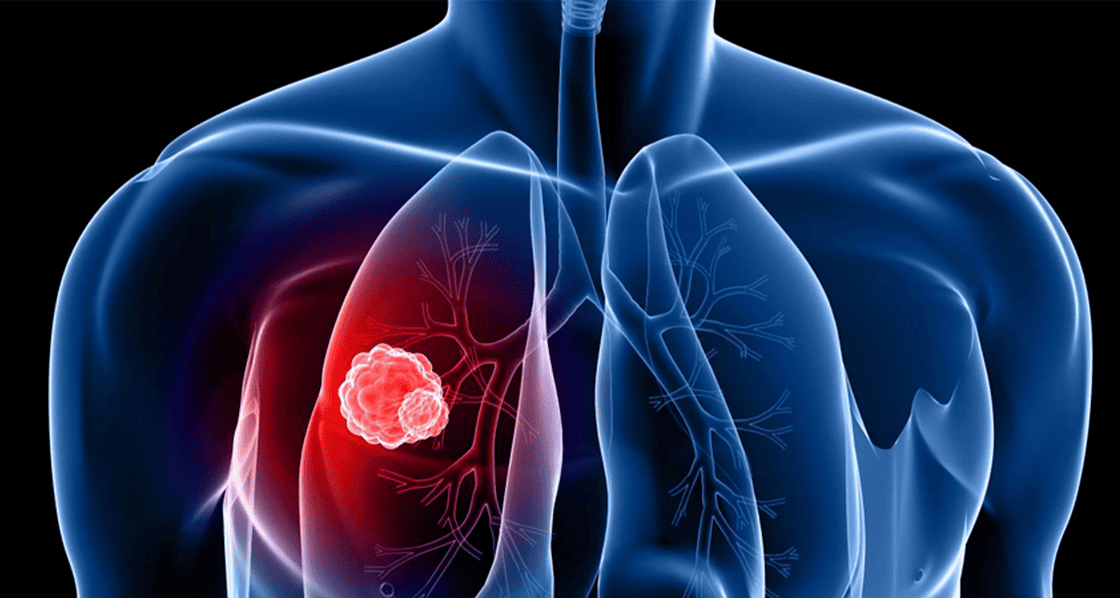
Inhaling radon gas exposes individuals to radioactive particles that can damage lung tissue, leading to serious health consequences.
Health Impacts of Radon Exposure
1. Lung Cancer Risk
Radon exposure is a leading cause of lung cancer, second only to smoking. The radioactive particles emitted by radon can damage lung cells, increasing the risk of cancer development.
Smokers face an even higher risk, as radon exposure compounds the carcinogenic effects of tobacco smoke, making it imperative for smokers to address radon levels in their living spaces.
2. Chronic Lung Diseases
Apart from lung cancer, radon exposure can contribute to the development of chronic lung diseases such as emphysema, chronic interstitial pneumonia, and pulmonary fibrosis.
These conditions can significantly impact respiratory function and overall health, underscoring the importance of mitigating radon exposure to prevent long-term health complications.
Scientific Evidence and Health Implications
Scientific research has unequivocally established the link between radon exposure and lung cancer.
Studies have shown that prolonged exposure to elevated radon levels significantly increases the risk of lung cancer, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to reduce radon concentrations in indoor environments.
While the association between radon exposure and other health issues like childhood leukemia is less clear, the potential risks warrant attention and further investigation.
Symptoms and Long-Term Effects
Unlike some environmental hazards that cause immediate health problems, radon exposure often manifests its effects over the long term.
Symptoms of lung cancer related to radon exposure, such as persistent coughing, shortness of breath, and wheezing, may not surface for years, highlighting the insidious nature of this health risk.
Early detection and mitigation of radon exposure are essential for preventing adverse health outcomes down the line.
Mitigation Strategies
Testing for radon levels in homes and workplaces is the first step in mitigating the health risks associated with radon exposure. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends maintaining indoor radon levels below 4 picocuries per liter (pCi/L) to minimize health risks.
If elevated radon levels are detected, various mitigation strategies can be employed, including:
- Sealing cracks and openings in foundations and walls to prevent radon entry
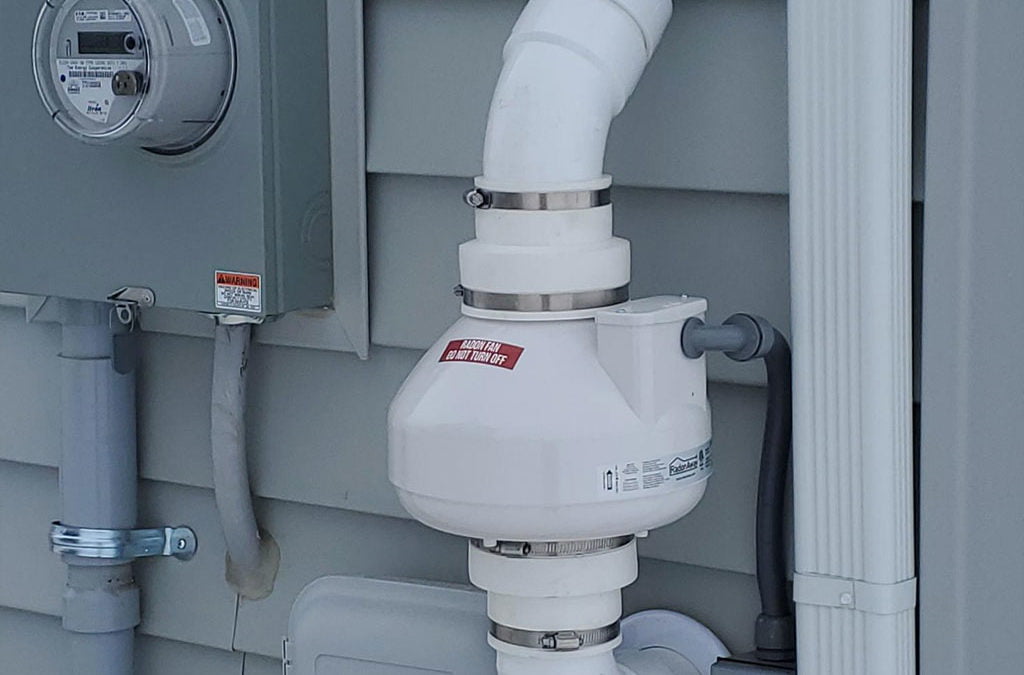
- Installing radon mitigation systems such as sub-slab depressurization to vent radon gas outdoors
- Improving ventilation in enclosed spaces to reduce radon buildup
Conclusion
Radon exposure poses a significant health risk, particularly in indoor environments where concentrations can accumulate to dangerous levels. By understanding the health impacts of radon exposure, recognizing the symptoms and long-term effects, and implementing effective mitigation strategies, individuals can protect themselves and their families from the harmful effects of this silent but potent threat. Prioritizing radon testing and mitigation is a proactive step toward creating healthier indoor environments and reducing the incidence of radon-related health issues.
In conclusion, raising awareness about radon exposure and its health implications is essential for promoting public health and well-being. By taking proactive measures to mitigate radon levels and reduce exposure, individuals can safeguard their health and create safer living environments for themselves and future generations.
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize radon testing and mitigation to combat this invisible yet significant health risk.