Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that can pose significant health risks if it accumulates in high concentrations in indoor environments. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, making it undetectable without specific testing measures. Given its potential to cause lung cancer, understanding how to effectively control and mitigate radon levels in homes and buildings is crucial.
This article delves into how radon mitigation systems work, exploring various components and techniques aimed at radon reduction, including system design, installation, maintenance, and the effectiveness and benefits of these systems.
Table of Contents
What is Radon?
Radon gas originates from the natural breakdown of uranium in soil, rock, and water. It can enter buildings through cracks in floors, walls, and foundations, and if not properly managed, it accumulates and poses a health risk to occupants. Prolonged radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking.
Testing for Radon
The first step in managing radon is through effective testing, which helps determine the radon levels present in an environment. Radon testing is a simple process that can be done using a variety of short-term and long-term kits available on the market.
If radon levels are found to be high (typically above 4 picocuries per liter, or pCi/L), it necessitates taking steps toward radon mitigation.
Radon Mitigation System Design and Components
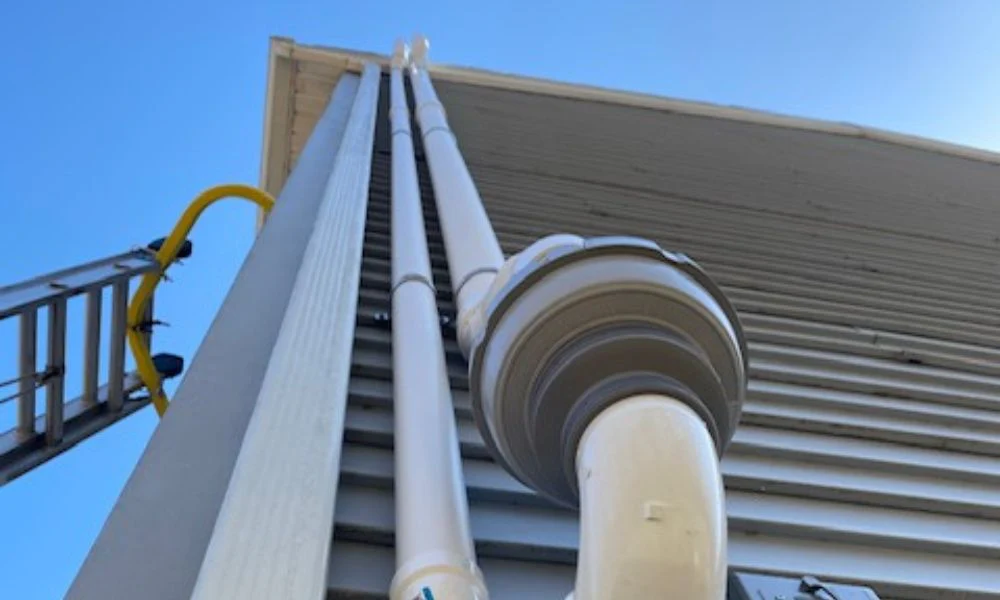
A radon mitigation system is designed to reduce radon concentrations in the indoor air of residential or commercial buildings. The typical radon mitigation system includes several key components:
- Radon Suction Point(s): This is where the system begins to draw radon from beneath the structure. Depending on the building’s foundation, one or more suction points might be necessary.
- Radon Piping: PVC or other types of piping are used to direct the radon gas from the suction point(s) to the outside.
- Radon Fan: A fan is crucial for the effectiveness of the system, creating a pressure differential that pulls radon from under the building and expels it outside.
- Radon Sealing: Sealing cracks and other openings in the foundation helps to reduce radon entry and improve the system’s efficiency.
Installation and Maintenance of Radon Mitigation Systems
Installation of a radon mitigation system is a task typically performed by certified professionals. The process involves strategic planning to determine the best location for suction points and the routing of pipes. The system must adhere to local radon mitigation system standards and regulations to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Once installed, regular maintenance and monitoring are crucial to ensure the system functions correctly. This includes checking system components like the fan and seals, and periodic radon testing to ensure levels remain low. Radon mitigation system maintenance ensures the long-term effectiveness of the system in reducing radon levels.
Effectiveness and Benefits of Radon Mitigation Systems
A properly installed and maintained radon mitigation system can significantly reduce radon levels in a building, often by up to 99%.
Lower radon levels mean a reduced risk of lung cancer for occupants, making these systems a critical component in public health within radon-prone areas.
Costs, Benefits, and Regulations
The cost of a radon mitigation system can vary depending on the size and design of the building, as well as local market conditions. However, the benefits, primarily the reduced health risk and increased safety, often outweigh the installation and maintenance costs.
Additionally, many jurisdictions have regulations and standards that guide the installation and operation of radon mitigation systems, ensuring that they provide the necessary safety measures.
Conclusion
Radon mitigation is a critical process for ensuring indoor air quality and public health. By understanding how radon mitigation systems function, property owners can make informed decisions about testing, system design, installation, and maintenance. Regular monitoring and adherence to regulatory standards play integral roles in ensuring these systems continue to operate effectively, providing a safer living or working environment for everyone.
In summary, radon mitigation systems are not just a building enhancement; they are a necessary investment in health and safety, designed to control and prevent the dangerous accumulation of radon in occupied spaces.
No related posts.